The articulation of your ankle joints facilitates both vertical and lateral movements of your foot. Encircling these joints are numerous ligaments that not only stabilize the bones but also establish connections between the leg bones and the foot bones.
With every step you take, your feet and ankles bear the weight of your entire body. Consider the additional stress they endure during activities like running or jumping, where the impact significantly increases, subjecting your ankle joints to forces equivalent to multiple times your body weight. Consequently, it’s not surprising that these joints are susceptible to injuries.
Ankle discomfort can stem from various sources, such as an injury like a stress fracture or an ankle sprain, or a medical condition like rheumatoid arthritis. The sensation could range from sharp, shooting pains to dull, persistent aches, contingent upon the underlying cause. Outlined below are the primary culprits behind ankle pain.
Unraveling the Common Triggers of Ankle Pain
The Hidden Danger: Stress Fractures
A prevalent trigger of ankle pain is a condition known as stress fractures. Stress fractures can be accurately described as microfractures, essentially minute cracks in the bone. These fractures aren’t born from a sudden impact or traumatic injuries but develop progressively.
Stress fractures are frequently an outcome of constant overuse or repetitive activities that don’t allow the bone to recuperate or heal. The act of constantly exerting pressure on the same bone, specifically the ankle in this context, can lead to these small scale fractures.
While it may not seem like a big deal, these microfractures can result in significant discomfort and pose a threat to one’s mobility. The key to managing stress fractures effectively is familiarizing oneself with their causes and symptoms.
Engagement in sports like football, basketball, or long-distance running, which require repeated movements, can make one susceptible to stress fractures as it puts the ankle bone under continuous strain. Other contributing factors could include nutritional deficiencies or a sudden increase in physical activity.
To recognize and treat stress fractures early, pay close attention to:
- Persistent pain in the ankle that worsens with activities but eases with rest;
- Swelling or tenderness around the affected area;
- Possible bruising.
Prompt medical intervention can go a long way in preventing the condition from worsening and ensuring speedy recovery. It’s crucial to rest the affected area, use protective footwear, and gradually reintroduce physical activity under a professional’s guidance to avoid reinjury. Also, discover effective plantar fasciitis exercises to relieve pain and improve mobility. Say goodbye to discomfort with these helpful exercises!
Decoding a Common Ankle Pain Culprit: Achilles Tendinopathy
Achilles Tendinopathy makes its way onto the list of usual suspects behind persistent ankle pain. This degenerative ailment sets in motion a gradual decay of the Achilles tendon – the robust tendon connecting your calf muscles to your heel bone.
One of the key contributors to Achilles tendinopathy is the incessant wear and tear of the tendon structures. This is often a product of repetitive overuse, such as engaging in high-impact sports, or a natural outcome of the ageing process which makes tendons less flexible and more prone to injury.
It’s crucial to understand that this condition doesn’t appear overnight. Continued strain and lack of adequate rest or rehabilitation can make the tendon vulnerable to this degenerative disease.
Key characteristics to look for if suspecting Achilles Tendinopathy:
- A dull or sharp pain along the back of your ankle, typically worse during or after physical activities;
- Stiffness in the heel area, especially noticeable when taking the first steps in the morning;
- Swelling in the lower part of the leg or around the heel.
Managing Achilles Tendinopathy can be multi-pronged. Here is what one can do to ease the discomfort and prevent further damage:
- Lower the intensity and frequency of physical activities causing stress on the tendon;
- Incorporate strength training and stretching exercises focused on the calf muscles into the routine;
- Use of ice packs to manage pain and swelling on affected area;
- Consider supportive shoes or orthotics to reduce strain on the tendon;
- Consultation with a physical therapist or a specialist for personalized care and rehabilitation strategies.
Ignoring the signs of Achilles Tendinopathy can prolong the recovery period and potentially lead to more severe conditions like the rupture of the Achilles tendon. Therefore, it’s vital to listen to your body, respect its limits, and seek professional help as soon as persisting discomfort is experienced.
A Closer Look At the Leading Cause of Heel Pain in Children: Sever’s Disease
Sever’s Disease, or calcaneal apophysitis, is a common source of heel discomfort frequently seen in children and young teens. Contrary to the ominous impression that the term ‘disease’ might cast, it’s important to clarify that Sever’s Disease is not a ‘disease’ in the traditional sense. It is essentially a painful bone disorder due to inflammation in a growth plate located in the heel.
During adolescence, rapid growth spurts often result in uneven development of the bone and muscles, and the heel bone tends to grow faster than the surrounding muscles and ligaments. This uneven pace can cause the Achilles tendon, attached to the heel bone, to pull on the heel’s growth plate, causing inflammation and pain – bread and butter symptoms of Sever’s Disease.
Sever’s Disease typically affects adolescents who are active in sports, particularly those involving a lot of running and jumping on hard surfaces, as this can amplify the stress on the heel’s growth plate.
Identifiable signs of Sever’s Disease include:
- Heel pain that exacerbates during or after physical activities;
- Limping or walking on toes to avoid heel pressure;
- Swelling or redness in the heel;
- Stiffness or discomfort in the feet upon waking.
A multi-faceted approach to managing Sever’s Disease ensures optimal recovery:
- Reducing or modifying physical activities that amplify heel pain;
- Applying ice to the affected area to alleviate pain and inflammation;
- Using heel lifts or arch supports in shoes for additional cushioning and support;
- Regular calf muscle stretches and exercises to enhance muscle flexibility;
- Over-the-counter pain medications, if advised by a healthcare provider.
This condition is temporary, and children eventually outgrow Sever’s disease when their heel bones fully mature. However, it’s vital to not ignore persistent heel pain. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment contribute greatly to faster recovery and preventing complications. Always consult a healthcare practitioner when dealing with prolonged symptoms.
Understanding the Impact of Pregnancy on Foot Health
Pregnancy, a significant chapter in a woman’s life, can bring with it a slew of bodily changes. These transformations encompass not just the visible enlarging of the belly but also numerous musculoskeletal changes that may cause discomfort in areas you might least expect, including your feet and ankles.
During pregnancy, the body naturally gains weight to support the growing fetus. This weight gain can substantially increase the load on the feet, leading to potential foot and ankle discomfort. The lower extremities, especially the ankles, may start to swell. This is due to fluid retention and increase in blood volume, which are normal occurrences but can cause discomfort.
In addition, hormonal changes during pregnancy can loosen the ligaments and joints across the body, including those in your feet. This loosening may lead to a condition called ‘Pregnancy-Induced Flat Feet,’ which might result in foot and ankle pain, and sometimes have a lasting effect post-pregnancy.
Typical indications of foot-related issues during pregnancy may include:
- Increased foot size or width;
- Swelling of the foot or ankle;
- Arch or heel pain;
- Over-pronation or flat feet.
To maintain foot health during pregnancy, consider the following recommendations:
- Wear comfortable and supportive footwear that accommodates changes in foot size;
- Keep the feet elevated to alleviate swelling;
- Stay hydrated to reduce fluid retention;
- Incorporate gentle exercises and stretches to enhance blood circulation;
- Use orthotic inserts if recommended by a healthcare professional;
- Avoid standing for prolonged periods.
Remember, while foot and ankle pain in pregnancy may be common, it shouldn’t be overlooked. If discomfort is persistent or escalates, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for tailored advice and treatment. Pregnancy is a time to take extra care of oneself, and foot health plays a pivotal role in ensuring the ability to comfortably enjoy this incredible journey.
Decoding Osteoarthritis: How It Impacts Your Joints
Osteoarthritis, often referred to as ‘wear and tear’ arthritis, is a degenerative joint disorder that results from the progressive deterioration of cartilage, the elastic tissue that acts as a cushion between bones at the joints.

Cartilage serves a critical role in ensuring smooth, frictionless movement of joints. However, with osteoarthritis, this protective cartilage erodes over time, causing the ends of the bones to rub together. This bone-on-bone contact can lead to significant discomfort, swelling, and difficulty in joint mobility.
Although osteoarthritis can impact any joint in the body, it most frequently affects those that bear weight over the years, such as the knees, hips, and ankles. Age, obesity, injuries, and genetics can all contribute to the development of this condition.
Charactertics of osteoarthritis include:
- Joint pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest;
- Stiffness in the joint, especially in the morning or after a period of inactivity;
- Swelling around the affected joint;
- Difficulty moving the joint and a decreased range of motion;
- A grating sensation during joint movement.
Managing osteoarthritis effectively involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical treatments:
- Regular low-impact exercise like swimming, walking, or cycling to help maintain joint mobility and reduce stiffness;
- Weight management to reduce pressure on weight-bearing joints;
- Use of over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medicines, as recommended by a healthcare provider;
- Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the joint and improve flexibility;
- Application of heat or cold to the affected area to alleviate pain and swelling;
- Use of assistive devices like canes or shoe inserts for additional support and to enhance mobility.
While osteoarthritis can alter the quality of life, adopting proactive measures can control its progression and ensure the maintenance of active lifestyles. Remember, early detection and appropriate treatment strategies under the guidance of a healthcare provider can significantly ease the journey with osteoarthritis.
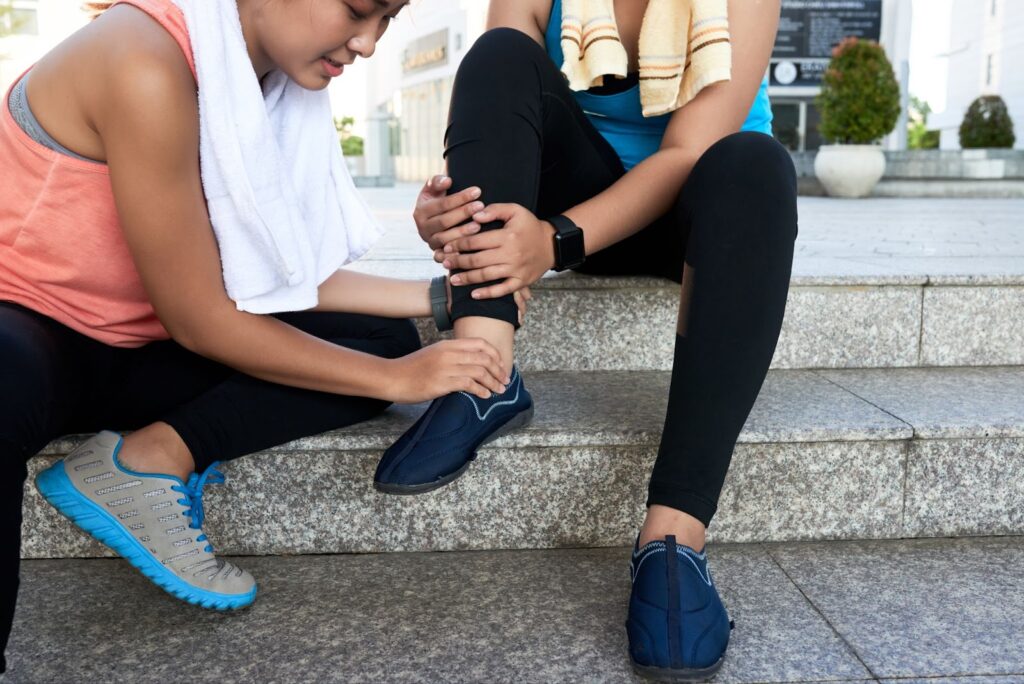
Navigating Through The Common Occurrence of Ankle Sprains
Ankle sprains, frequently occurring in sport-related activities as well as in routine daily tasks, are one of the most prevalent musculoskeletal injuries. They occur when the ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limit or tear due to a sudden twist, turn, or roll of the foot. This often happens when the foot lands awkwardly or the person lands on an uneven surface or object.
While minor sprains can often be managed at home with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE method), more severe cases may require medical intervention. Key indicators of a sprained ankle include:
- Immediate, intense pain in the ankle;
- Swelling and bruising around the area;
- Difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot;
- Limited range of motion of the ankle joint;
- Localized tenderness upon touch.
To manage an ankle sprain effectively and promote healing, consider the following steps:
- Rest the injured ankle to reduce further strain and promote healing;
- Apply an ice pack to the area to decrease swelling and relieve pain;
- Use an elastic compression bandage to minimize swelling;
- Elevate the foot above the level of the heart as often as possible to reduce swelling;
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers, as recommended by a healthcare professional;
- Once the acute phase has passed, start gentle rehabilitation exercises to restore flexibility, strength, and balance of the ankle.
Prevention of ankle sprains is crucial, especially for those engaged in athletic activities or those who have previously experienced a sprain. Wearing supportive footwear, using ankle braces if required, warming up before exercise, being attentive to surrounding surfaces and maintaining a healthy day-to-day fitness level can help avoid this painful inconvenience.
Despite the common nature of ankle sprains, they shouldn’t be dismissed lightly. Neglecting proper treatment and care can lead to chronic ankle instability or prolonged pain. For severe sprains or if symptoms persist, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to assess the injury and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of ankle joints and the potential causes of ankle pain is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing the various sources of discomfort and seeking appropriate medical guidance, individuals can effectively manage ankle-related issues and promote long-term musculoskeletal health. Whether it’s through targeted therapies or consultations with specialized professionals, addressing ankle pain comprehensively can lead to improved mobility and overall well-being.