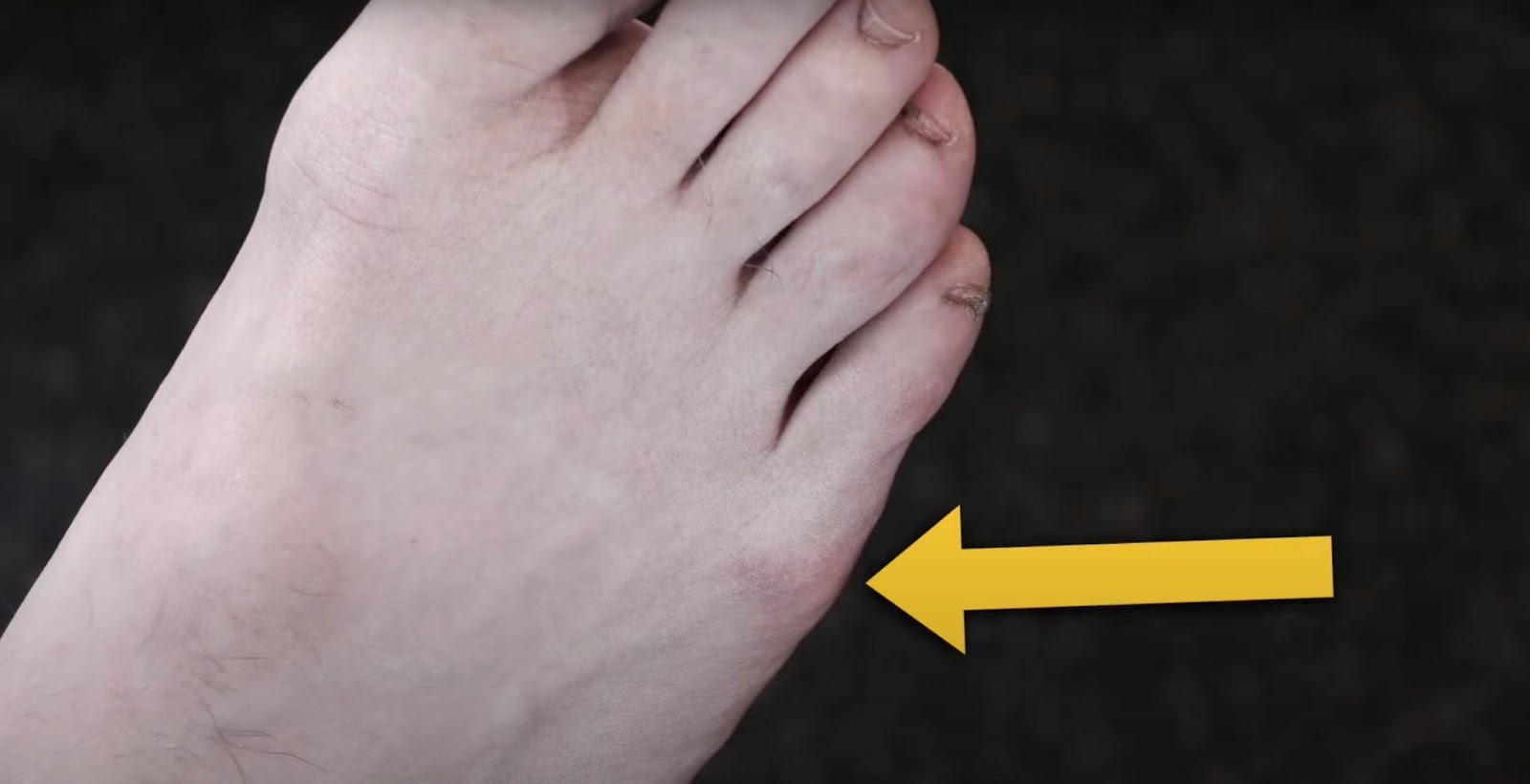
Iselin’s disease, a condition that affects the feet of growing children, is characterized by a painful and protruding bone on the outside of the foot. While it may sound alarming, this temporary growth-related issue is a common occurrence during childhood development.
Key Questions Addressed in this Article:
- What is Iselin’s disease and how does it affect growing children?;
- What are the causes and symptoms of Iselin’s disease?;
- What are the risk factors associated with Iselin’s disease?;
- How is Iselin’s disease diagnosed?;
- How can parents recognize if their child has Iselin’s disease?;
- What are the treatment options available for Iselin’s disease?;
- What potential complications can arise from ignoring Iselin’s disease?;
- How can Iselin’s disease be prevented to ensure children’s foot health?
What Is Iselin’s Disease?
Iselin’s disease, also known as traction apophysitis, is a type of growing pain that affects the feet in children. Specifically, it targets the outside border of the foot at the bony ‘bump’ known as the ‘styloid process’. This bump is located at the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, approximately halfway along the outer foot.
The Temporary Nature of Iselin’s Disease
Despite its ominous-sounding name, Iselin’s disease is a temporary condition that cannot recur once the bones reach maturity and stop growing. It is a painful but ultimately harmless growth-related issue that resolves itself as the child’s skeletal development progresses.
The Anatomical Location
The styloid process, where Iselin’s disease manifests, is a prominent bony protrusion on the outside of the foot. It serves as an attachment point for the peroneus brevis tendon, a muscle responsible for foot eversion (outward rotation) and stability during weight-bearing activities.
What Causes Iselin’s Disease?
To understand the underlying cause of Iselin’s disease, it is essential to examine the bone growth process in children.
Bone Growth and Growth Plates
Before bones mature, they contain specific cartilaginous areas called ‘growth plates’ that act as construction sites for new bone cell growth. These growth plates are weaker than the rest of the bone, making them more susceptible to irritation and tension during physical activity.
Muscle Tension and Growth
As children grow, their muscles lengthen and strengthen to keep up with the body’s growth. During this process, the muscles experience periods of tightness, which can lead to increased tension on the bones they attach to, particularly near the growth plates.
In the case of Iselin’s disease, the peroneus brevis tendon attaches to the styloid process, which is located near a growth plate. When this tendon pulls and places tension on the bone during physical activity, it can irritate and cause pain in the growth plate, leading to the characteristic symptoms of Iselin’s disease.
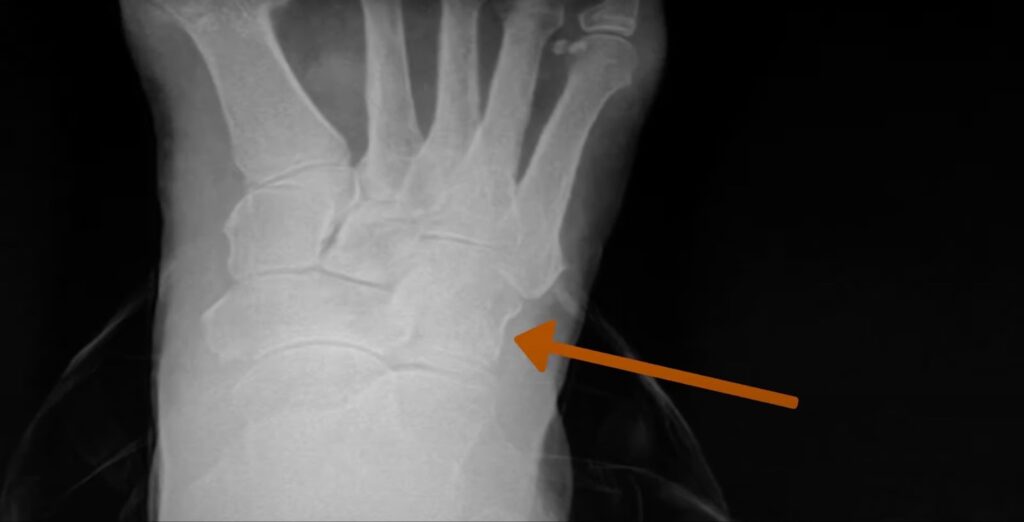
Symptoms
The primary symptom of Iselin’s disease is pain on the outside border of the foot during physical activity. Additional symptoms may include:
Pain and Swelling
- Pain can ease with rest and may come and go for months or even years;
- Swelling may be present on the outside of the foot, at the base of the fifth metatarsal.
Altered Gait
- Children may walk with a limp or altered gait to reduce pain and pressure on the outside of the foot.
Lack of Injury or Infection
- A notable symptom of Iselin’s is the absence of any identifiable injury history, trauma, or infection that could explain the symptoms.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing Iselin’s disease, including:
Tight Muscles
- Tight calf or peroneal muscles may increase tension on the growth plate during physical activity.
Repetitive Movements
- Activities involving repeated changes in direction or heavy plyometric exercises can increase tension at the insertion of the peroneus brevis tendon.
Previous Injuries
- A history of inversion injuries (rolling the ankle inward) may predispose individuals to Iselin’s disease.
Diagnosing
Diagnosing Iselin’s disease can be done based on the patient’s history and a physical assessment by a healthcare professional.
Differential Diagnosis
- Confidently diagnosing Iselin’s can be challenging due to other pathologies with similar presentations, such as stress fractures, avulsion fractures, or Jones’ fractures.
Imaging Tests
- X-rays can be offered to rule out other possible diagnoses;
- Ultrasound imaging may be used to rule out coinciding muscle or tendon injuries.
How to know if your child has Iselin’s disease
If you suspect your child may have Iselin’s disease, it is crucial to seek an evaluation from a podiatrist or healthcare professional. Pain in children should never be ignored, as it may indicate an underlying condition that requires proper diagnosis and treatment.
Signs to Look For
- Persistent pain on the outside of the foot during physical activity;
- Swelling or tenderness around the bony protrusion on the outer foot;
- Limping or altered gait to alleviate pain.
Seeking Professional Evaluation
Even if the cause is not Iselin’s disease, a podiatrist can uncover and diagnose the true cause of the pain and provide appropriate treatment. Early intervention is key to preventing further complications and ensuring your child’s foot health.
Treatment
At The Feet People, we understand that foot pain in children can significantly impact their quality of life and physical activity levels. Our approach to treating Iselin’s disease is multifaceted and tailored to each individual case.
Immobilization and Rest
- Temporary immobilization using a cast, boot, or splint may be recommended to allow the affected area to rest and heal;
- Activity modification and rest from aggravating activities are essential during the acute phase.
Pain Management
- Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or anti-inflammatory drugs, may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort;
- Ice application can help reduce swelling and pain.
Physical Therapy
- Stretching and strengthening exercises may be prescribed to address muscle tightness and imbalances;
- Gait training and proprioceptive exercises can help improve foot mechanics and reduce stress on the affected area.
Orthotics and Supportive Footwear
- Custom-made orthotics can provide arch support and cushioning, reducing stress on the affected area;
- Supportive footwear with adequate cushioning and stability can help distribute forces more evenly across the foot.
Surgical Intervention
In rare and severe cases, surgical intervention may be considered if conservative treatments fail to provide relief. This may involve removing the inflamed section of the growth plate or addressing any underlying structural abnormalities.
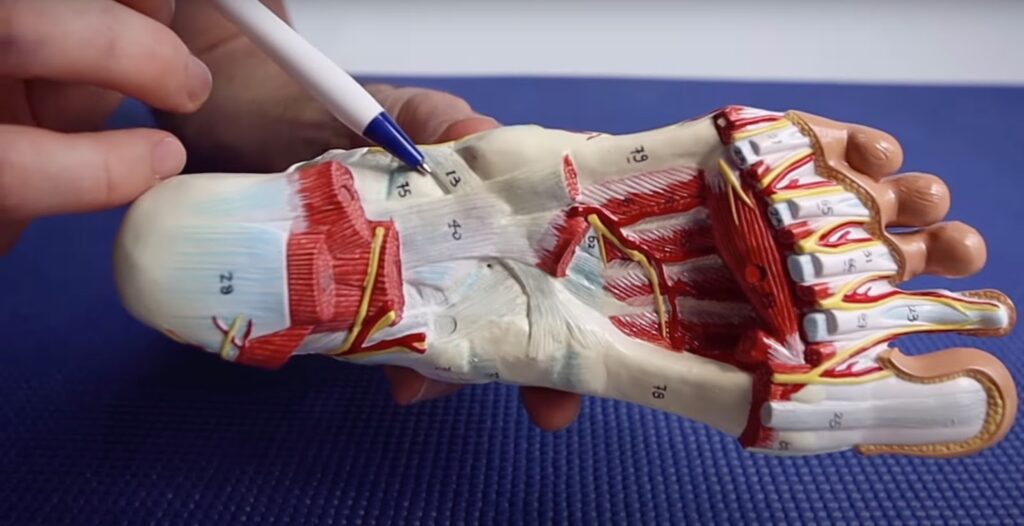
What Can Happen If I Ignore
While Iselin’s disease is generally a self-limiting condition, ignoring it or failing to seek proper treatment can lead to potential complications.
- Prolonged Pain and Disability: Untreated Iselin’s disease can result in persistent pain, limiting a child’s ability to participate in physical activities and negatively impacting their overall well-being;
- Compensatory Gait Patterns: Children may develop compensatory gait patterns to alleviate pain, which can lead to additional biomechanical issues and muscular imbalances;
- Delayed Healing and Recovery: Without proper treatment and rest, the inflammation and irritation may persist, prolonging the healing process and delaying recovery;
- Psychological Impact: Chronic pain and limitations can affect a child’s mental health, leading to frustration, decreased self-esteem, and potential social withdrawal.
Preventing Ways
While Iselin’s disease is a natural occurrence during growth and development, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk and prevent its occurrence or recurrence.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing well-fitting, supportive shoes with adequate cushioning can help distribute forces evenly across the foot, reducing stress on the affected area;
- Stretching and Strengthening: Incorporating regular stretching and strengthening exercises into a child’s routine can help maintain muscle flexibility and balance, reducing excessive tension on the growth plates;
- Activity Modification: Monitoring and modifying activities that involve repetitive or high-impact movements can help prevent excessive strain on the affected area;
- Gradual Increase in Activity Levels: When returning to physical activities after an episode of Iselin’s disease, it is essential to gradually increase the intensity and duration to allow the body to adapt and recover properly.
Conclusion
Iselin’s disease, while potentially concerning for parents, is a temporary and manageable condition that affects the feet of growing children. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and risk factors, parents and healthcare professionals can work together to provide appropriate treatment and preventive measures. With proper care and management, children can overcome Iselin’s disease and continue to engage in physical activities without limitations. Remember, early intervention and seeking professional evaluation are crucial for ensuring your child’s foot health and overall well-being. Incorporating specific exercises tailored for Achilles tendonitis can further aid in the recovery process, promoting strength and flexibility in the affected area.