Key Questions Explored in This Article:
- What Is Plantar Fasciitis?;
- What Causes Plantar Fasciitis?;
- How Do You Recognize the Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis?;
- How Is Plantar Fasciitis Diagnosed?;
- What Are the Treatment Options for Plantar Fasciitis?;
- What Self-Care Measures Can Help with Plantar Fasciitis?;
- What Happens If You Ignore Plantar Fasciitis?;
- How Can You Prevent Plantar Fasciitis?
Foot pain, especially that associated with plantar fasciitis, is a condition that affects a significant portion of the population, bringing attention to the crucial role of foot health in overall well-being and mobility. Characterized by sharp, debilitating pain in the heel or the bottom of the foot, plantar fasciitis is more than just an inconvenience; it’s a signal from the body that the intricate structure of the foot is under distress. This article seeks to shed light on plantar fasciitis, diving into its causes, symptoms, and the multifaceted approach required for effective management and prevention. By understanding this common foot ailment, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining foot health, ensuring that their feet—those fundamental supports that carry us through life’s activities—remain strong and pain-free. Whether you’re an athlete, a weekend warrior, or someone whose lifestyle demands long hours on your feet, this comprehensive guide offers insights into navigating the challenges of plantar fasciitis and fostering a foundation of foot health.
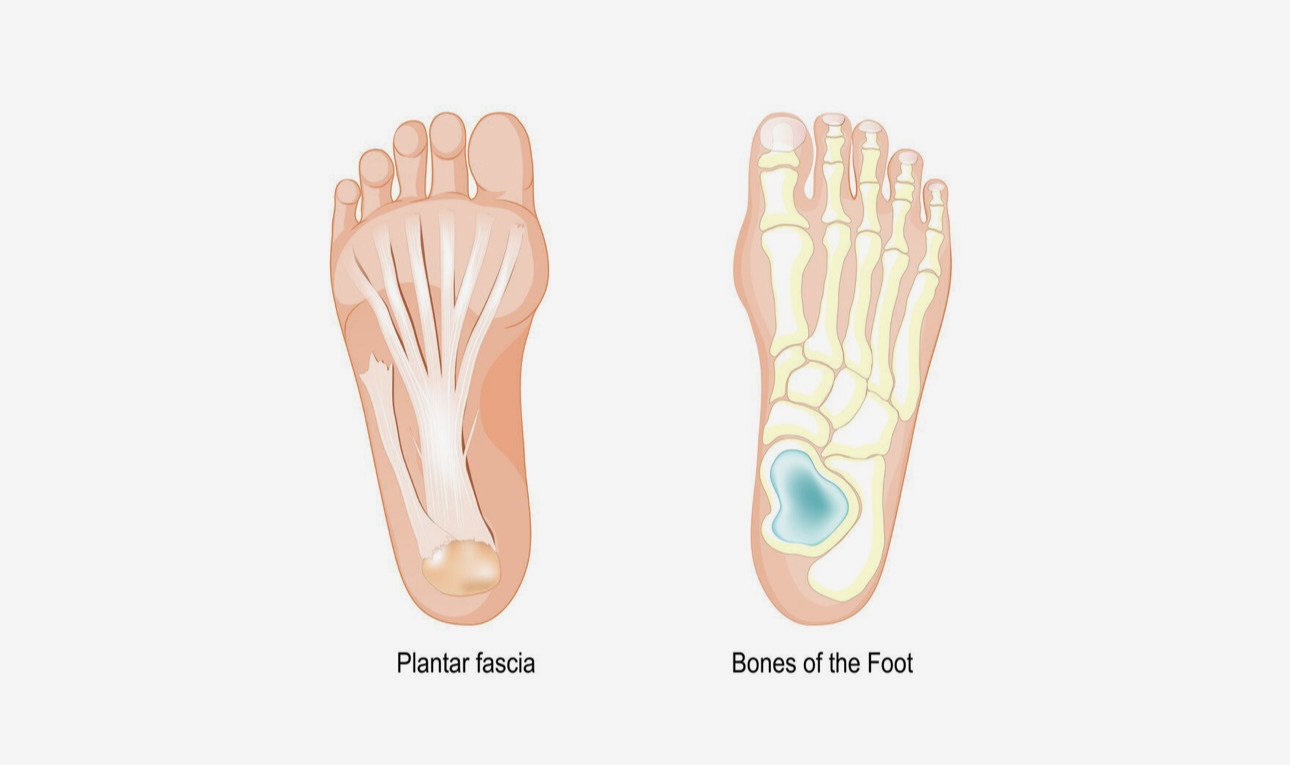
What is Plantar Fasciitis?
In the realm of foot health, plantar fasciitis emerges as a common ailment that afflicts many. This condition stems from the inflammation of the plantar fascia, a robust band of tissue that spans the underside of the foot, anchoring at the heel and extending to the toes. This fibrous band plays a crucial role in foot stabilization and support during the myriad activities of daily life. However, when the plantar fascia is subjected to excessive strain or overload, it can become inflamed, leading to the characteristic pain and discomfort associated with plantar fasciitis. Typically, this condition develops when alterations occur in an individual’s daily or exercise routines, imposing an unmanageable load on the plantar fascia.
Often, individuals with plantar fasciitis may also experience the formation of heel spurs, although these spurs are usually not the primary source of pain and can often be asymptomatic.
Causes & Risk Factors
The primary culprit behind plantar fasciitis is the alteration in foot loading patterns. When the heel bone and surrounding soft tissue are subjected to repetitive high loads, they become fatigued, reducing their shock-absorbing capabilities. This fatigue can lead to plantar fasciitis. Risk factors are multifaceted and include overuse, inappropriate footwear, insufficient lower limb strength, mobility and flexibility, muscle imbalances, rigid feet, excessive inward rolling of the feet (overpronation), differences in leg length, abnormal walking or running patterns, weight gain, sedentary lifestyle, and occupations or hobbies that require prolonged standing. Age also plays a role, as tissues become less elastic over time.
Symptoms
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis can severely impact one’s quality of life. The pain, primarily localized around the heel, is most intense during the first steps in the morning or after periods of rest. It may manifest as a dull, sharp, or intermittent ache, often described as a “bruised” feeling. Additional symptoms include difficulty bearing weight upon waking, stiffness and tightness in the arch, and a gradual improvement of pain with initial activity that worsens again with prolonged activity.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing plantar fasciitis requires a thorough physical assessment by a podiatrist, who may also utilize ultrasound imaging to evaluate the extent of the injury. This careful examination is crucial to differentiate plantar fasciitis from other causes of heel pain.
Treatment
Treatment strategies for plantar fasciitis are varied, aiming for a rapid and effective recovery. These can include the RICE protocol (rest, ice, compression, elevation), strengthening and stretching exercises, training modifications, supportive footwear, custom orthotics, foot and ankle strapping, shockwave therapy, dry needling, anti-inflammatory medications, and foot mobilization techniques. An individualized treatment plan is essential for the best outcomes.
Self-Care Tips
Patients are encouraged to engage in self-care practices such as performing foot alphabet exercises before getting out of bed, alternating daily activities to reduce impact, avoiding barefoot walking, and trying at-home exercises like calf raises. These measures, alongside professional treatment, can significantly aid in recovery.
Ignoring Plantar Fasciitis
Neglecting plantar fasciitis can lead to a prolonged recovery period and potentially severe complications, such as tearing or rupturing of the plantar fascia, necessitating extended immobilization in a moon boot.
Prevention
Proactive measures to prevent plantar fasciitis include wearing appropriate footwear, reducing barefoot time, strengthening lower leg muscles, getting professional advice on movement patterns and footwear, warming up before exercise, and gradually increasing training intensity. These preventive strategies can markedly decrease the risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plantar fasciitis is a prevalent condition that poses significant challenges to individuals’ mobility and quality of life. Stemming from the inflammation of the plantar fascia, this ailment underscores the importance of foot health and the intricate balance required to maintain it. Recognizing the multifactorial causes and risk factors, from lifestyle choices to biomechanical discrepancies, is essential in both prevention and treatment. Through a comprehensive approach that includes professional diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and proactive self-care measures, individuals can effectively manage plantar fasciitis.
Emphasizing prevention through appropriate footwear, strength conditioning, and mindful activity adjustments can substantially mitigate the risk of onset. Ultimately, understanding and addressing the underlying factors of plantar fasciitis not only facilitates recovery but also champions the broader endeavor of sustaining foot health and overall well-being.
FAQs:
Plantar fasciitis can improve on its own over time, especially with rest and reduced activity. However, without addressing the underlying causes and implementing appropriate treatments, symptoms can persist or recur. Early intervention can significantly speed up recovery and prevent chronic issues.
Recovery times for conditions like plantar fasciitis vary widely depending on the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and the effectiveness of the treatment strategies employed. On average, individuals may start to experience improvement within a few weeks to several months after beginning treatment. However, it’s important to note that for some, complete recovery can take longer, especially if the condition was severe or chronic before treatment commenced. Consistent adherence to prescribed treatment plans, which may include physical therapy exercises, the use of orthotics, rest, and possibly anti-inflammatory medications, is crucial for facilitating recovery. Preventive measures, such as wearing appropriate footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that place excessive stress on the feet, are equally important in preventing recurrence of symptoms. Engaging in regular, gentle stretching exercises for the foot and calf muscles can also support the healing process and improve flexibility, further contributing to a faster and more effective recovery. Patients are encouraged to communicate openly with their healthcare providers about their progress and any concerns they may have during their recovery journey, ensuring adjustments can be made to their treatment plan as needed for optimal outcomes.
Yes, footwear that provides proper arch support, cushioning, and a comfortable fit can help alleviate plantar fasciitis symptoms and prevent further strain on the plantar fascia. Orthopedic shoes or those specifically designed for plantar fasciitis sufferers are often recommended.
Certain high-impact exercises and activities that put excessive strain on the heel and arch can indeed worsen plantar fasciitis symptoms. Activities such as running on hard surfaces, jumping, and other forms of vigorous exercise can increase inflammation and pain due to the added stress on the plantar fascia. It’s critical to modify exercise routines to include low-impact activities, such as swimming, cycling, or using an elliptical trainer, which minimize stress on the feet while allowing you to stay active. Additionally, incorporating specific stretching and strengthening exercises that target the Achilles tendon and the muscles in the foot can provide support and reduce tension in the plantar fascia. These exercises aim to improve flexibility and strength in the affected area, thereby mitigating symptoms and preventing further injury. Foot orthotics and supportive footwear can also play a significant role in alleviating stress on the plantar fascia during physical activity. Consulting with a healthcare professional experienced in treating plantar fasciitis can help you develop an exercise plan that is safe and effective for your condition, ensuring that your path to recovery is optimized without exacerbating the problem.
If you experience persistent heel pain that does not improve with rest, self-care measures, and modifications to your activities, or if the pain becomes so severe that it interferes with your daily activities, it’s advisable to seek medical advice. Heel pain that persists for more than a few weeks, worsens over time, or occurs regularly upon waking or starting an activity should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. A podiatrist or orthopedic specialist can provide a comprehensive diagnosis, utilizing tools such as physical exams, imaging studies (like X-rays or MRIs), and assessing your foot mechanics to identify the extent of the problem. They can then recommend effective treatments, which may include physical therapy, custom orthotics, medication, or in some cases, more advanced interventions like shockwave therapy or surgery. The goal is to create a recovery plan tailored to your specific needs, addressing not only the symptoms but also the underlying causes of plantar fasciitis. Early intervention is key to managing plantar fasciitis effectively, reducing the risk of chronic heel pain, and helping you return to your normal activities.