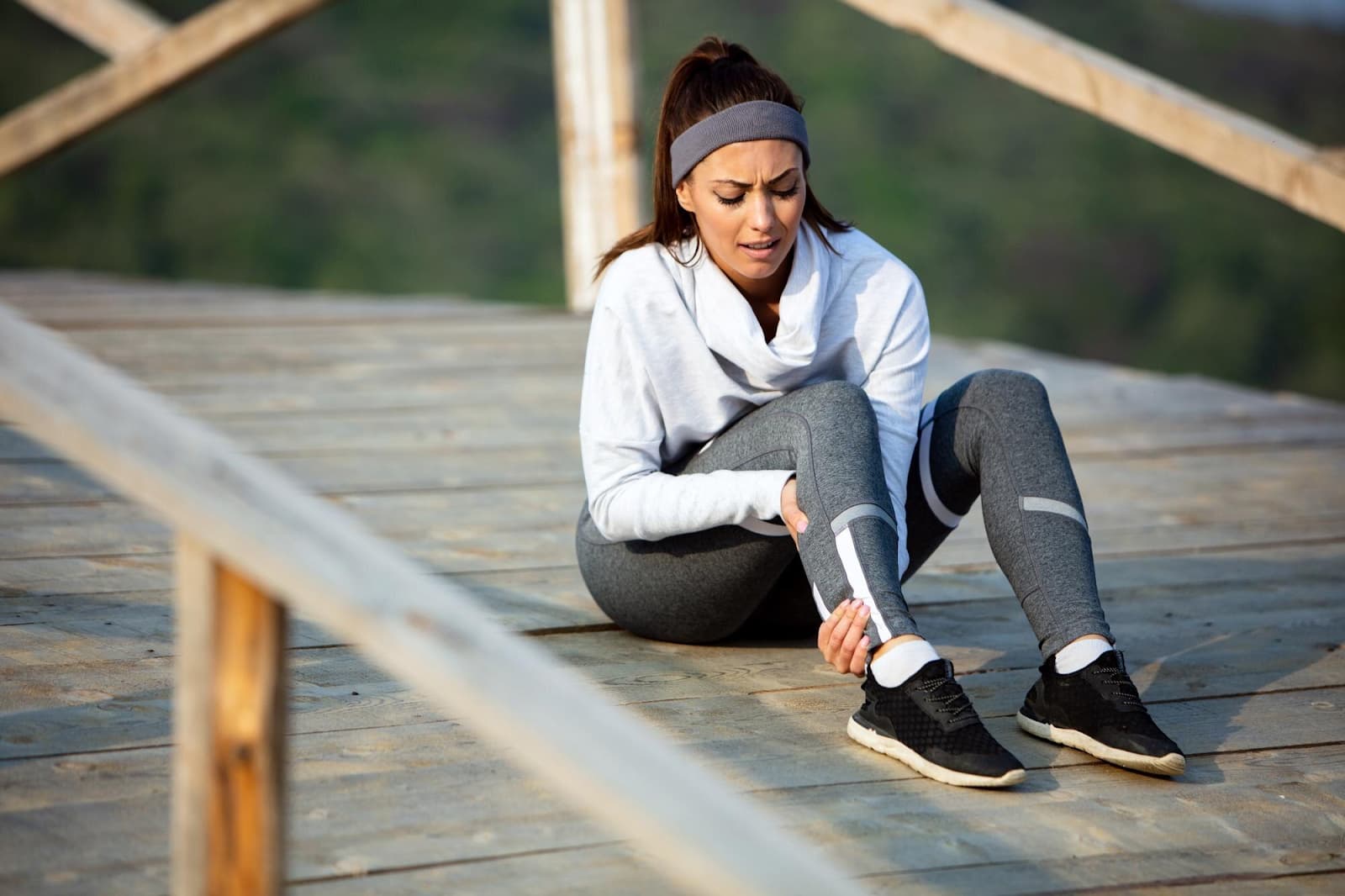
Ankle sprains are one of the most common musculoskeletal injuries, affecting individuals of all ages and activity levels. Whether due to sports activities, everyday accidents, or underlying conditions, ankle sprains can cause significant discomfort and impair mobility. Understanding the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures for ankle sprains is crucial for both athletes and the general population. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the various aspects of ankle sprains, including their causes, types, treatment methods, rehabilitation, prevention, and long-term management.
Understanding Ankle Sprains
Types of Ankle Sprains
Ankle sprains are typically categorized based on the severity of the injury and the specific ligaments involved. The two primary types of ankle sprains are:
- Inversion Ankle Sprains: This type of sprain occurs when the foot rolls inward, stretching the outer (lateral) ligaments of the ankle;
- Eversion Ankle Sprains: Eversion sprains happen when the foot turns outward, leading to damage to the inner (medial) ligaments of the ankle.
Common Ankle Sprain Causes
Ankle sprains often occur due to accidental sudden loss of balance, such as:
- Missteps on uneven surfaces;
- Awkward landings during physical activities;
- Sports-related incidents involving sudden changes in direction or impact.
Understanding the specific causes of ankle sprains can help individuals take preventive measures to reduce the risk of sustaining such injuries.
In addition to these common causes, it’s important to differentiate between a sprain and other ankle injuries, such as fractures, which may require different treatment approaches.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Ankle sprains manifest through various symptoms, including pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected ankle. While some cases may only involve mild discomfort and limited swelling, severe sprains can lead to significant instability and immobility.
Diagnosing an ankle sprain typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional, along with potential imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans to assess the extent of the injury and rule out any associated fractures.
Grading Ankle Sprains
Ankle sprains are graded based on their severity:
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| I | Mild sprain with slight stretching |
| II | Moderate sprain with partial tearing |
| III | Severe sprain with complete ligament tear |
Understanding the grading system helps in determining the appropriate course of treatment and estimating the recovery timeline.
Treatment Options
The management of ankle sprains depends on the severity of the injury and may include conservative measures or, in more severe cases, surgical intervention. Common treatment options for ankle sprains include:
- R.I.C.E. Protocol: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation to reduce pain and swelling;
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion;
- Bracing or Taping: Providing external support to the ankle to enhance stability during the healing process.
In cases where conservative treatments are ineffective or if there is significant ligament damage, surgical repair may be necessary to restore stability to the ankle joint.
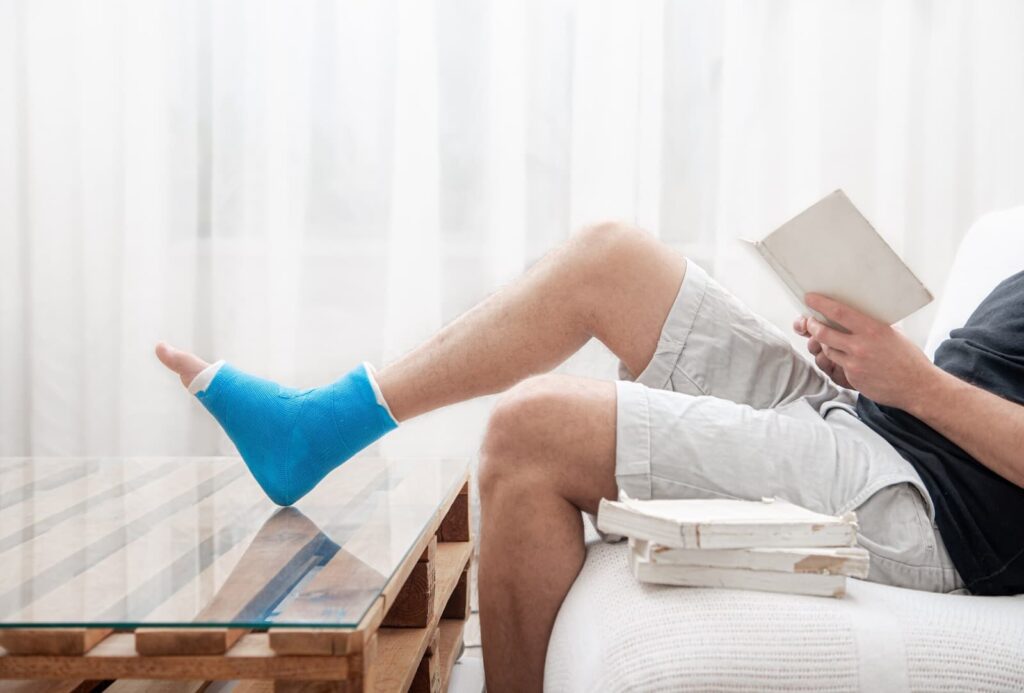

Rehabilitation and Long-Term Management
Importance of Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in the recovery process following an ankle sprain. It aims to restore function, strength, and flexibility while reducing the risk of recurrent injuries. The key components of ankle sprain rehabilitation include:
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gradual movements to improve flexibility and reduce stiffness;
- Strength Training: Targeted exercises to rebuild muscle strength around the ankle joint;
- Proprioception and Balance Training: Activities to enhance coordination and stability.
Preventing Recurrence
After experiencing an ankle sprain, individuals are at a higher risk of subsequent injuries. Therefore, implementing preventive strategies is essential to minimize the likelihood of recurrence. These strategies may include:
- Wearing supportive footwear;
- Using ankle braces during physical activities;
- Engaging in regular ankle-strengthening exercises.
By incorporating these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of re-injury and maintain long-term ankle health.
Long-Term Management and Complications
While many ankle sprains heal with appropriate care and rehabilitation, some individuals may experience lingering issues, such as chronic instability or recurrent swelling. Long-term management involves ongoing monitoring, periodic check-ups, and potentially additional interventions to address persistent symptoms.
Complications associated with ankle sprains may include:
- Chronic Instability: Persistent feeling of giving way or weakness in the ankle joint;
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Development of arthritis due to the initial injury and subsequent wear and tear on the joint.
Managing these complications often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic specialists, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals to optimize outcomes and quality of life for individuals with persistent ankle issues.
Preventive Measures for Ankle Sprains
Strengthening and Conditioning
Engaging in targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the ankle joint is crucial for enhancing stability and reducing the risk of sprains. Incorporating exercises that focus on balance, proprioception, and agility can significantly contribute to injury prevention.
Ankle-Strengthening Exercises
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Calf Raises | Standing on tiptoes and lowering the heels back down, targeting the calf muscles. |
| Ankle Circles | Rotating the ankle in circular motions to improve flexibility and range of motion. |
| Single-Leg Balance Drills | Balancing on one leg to improve proprioception and strengthen ankle stabilizing muscles. |
Regularly performing these exercises as part of a comprehensive fitness routine can help fortify the ankle joint and lower the risk of sprains during physical activities.
Footwear and External Support
Choosing appropriate footwear and utilizing external support, such as ankle braces or taping, can provide added stability and protection during athletic pursuits or activities involving repetitive movements. Supportive shoes with good traction and ankle support can significantly reduce the risk of twisting or rolling the ankle.
Factors to Consider in Footwear Selection
- Arch Support: Shoes with adequate arch support can help distribute pressure evenly across the foot;
- Ankle Stability: High-top shoes or those with reinforced ankle support can minimize excessive ankle movement.
By paying attention to footwear choices and using external support when necessary, individuals can mitigate the risk of sustaining ankle sprains during various physical endeavors.
Environmental Awareness and Injury Avoidance
Being mindful of environmental factors and potential hazards can greatly contribute to preventing ankle sprains. Simple precautions such as clearing cluttered walkways, avoiding slippery surfaces, and using caution during physical activities can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidental injuries.
Tips for Injury Avoidance
- Regular inspection of walking and exercise areas for potential hazards;
- Adhering to safety guidelines and proper technique during sports and recreational activities;
- Utilizing appropriate protective gear, such as ankle braces or guards, when engaging in high-risk physical pursuits.
By fostering environmental awareness and adhering to safety practices, individuals can create safer surroundings and minimize the risk of ankle sprains.
Conclusion
Ankle sprains are prevalent injuries that can have a substantial impact on an individual’s daily activities and overall quality of life, same as ingrown toenail. By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures associated with ankle sprains, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of sustaining such injuries and facilitate optimal recovery when they do occur. Through a combination of targeted exercises, environmental awareness, and appropriate medical care, the incidence of ankle sprains can be significantly reduced, allowing individuals to maintain strong and stable ankle joints for years to come.